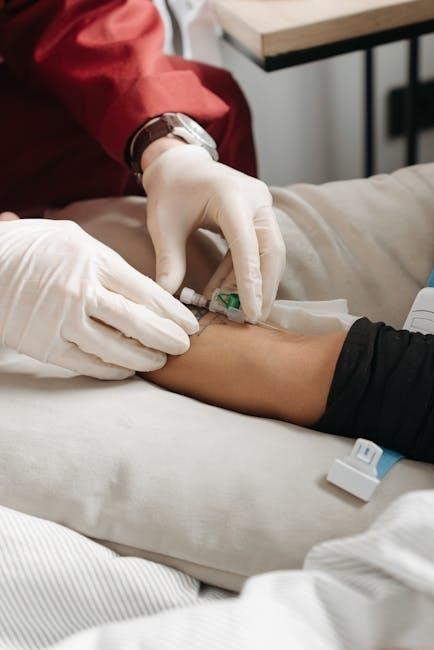
Ultrasound-guided IV insertion training is crucial for nurses, enhancing success rates, reducing complications, and improving patient comfort. It combines technical ultrasound proficiency with clinical expertise for optimal vascular access outcomes.
Importance of Ultrasound-Guided IV Insertion in Modern Nursing Practice
Ultrasound-guided IV insertion has become a cornerstone in modern nursing, significantly improving patient care and clinical outcomes. By enhancing accuracy and reducing complications, it addresses challenges like difficult venous access, common in patients with obesity, dehydration, or chronic conditions. This technique minimizes multiple insertion attempts, thereby decreasing patient discomfort and anxiety. Additionally, it promotes longer catheter patency, reducing the need for frequent replacements. The use of ultrasound aligns with current healthcare goals of optimizing efficiency, safety, and patient satisfaction. Its adoption is particularly vital in high-stakes settings, such as intensive care units, where timely and reliable vascular access is critical. Thus, ultrasound-guided IV insertion is not just an advanced skill but a essential tool in contemporary nursing practice.

Background on Traditional IV Insertion Methods
Traditional IV insertion relies on palpation and anatomical landmarks, but its effectiveness is limited in patients with challenging venous access, leading to higher failure rates and complications.
Limitations of Landmark-Based IV Insertion
Landmark-based IV insertion relies on palpation and anatomical knowledge, but it has significant limitations, particularly in patients with challenging venous access. Obesity, dehydration, and conditions like end-stage renal disease or peripheral vascular disease can make veins difficult to locate, leading to higher failure rates. Multiple attempts are common, increasing patient discomfort and the risk of complications such as nerve or artery damage. Additionally, landmark-based methods lack the precision needed for consistent success, especially in emergency or critically ill patients. These limitations highlight the need for alternative approaches, such as ultrasound guidance, to improve outcomes and reduce procedural complications.
Challenges in Difficult Venous Access (DIVA) Patients
DIVA patients present unique challenges for IV insertion due to factors like obesity, dehydration, or chronic conditions such as end-stage renal disease. Their veins are often deep, fragile, or scarred, making them hard to locate and access. Traditional methods frequently fail, leading to multiple attempts, increased pain, and patient anxiety. These challenges also heighten the risk of complications, including infiltration, thrombophlebitis, and nerve damage. Nurses must employ specialized skills and tools, such as ultrasound guidance, to overcome these obstacles and ensure successful IV placement. The ability to handle DIVA patients efficiently is critical for maintaining patient safety and comfort in clinical settings.
Benefits and Advantages of Ultrasound-Guided IV Insertion
Ultrasound-guided IV insertion offers higher success rates, improved patient comfort, and longer catheter patency compared to traditional methods, enhancing both safety and efficiency in clinical settings;
Higher Success Rates in IV Placement
Ultrasound-guided IV insertion significantly improves success rates, particularly in patients with difficult venous access. Studies demonstrate that ultrasound guidance increases first-attempt success compared to traditional landmark-based methods. This is attributed to real-time visualization, enabling precise needle placement and reducing anatomical uncertainties. In challenging cases, such as obese patients or those with peripheral vascular disease, ultrasound guidance enhances the ability to locate and access suitable veins. Additionally, it minimizes complications like hematoma formation and nerve injury. The use of ultrasound has been shown to decrease insertion attempts, reducing patient discomfort and procedural time. Training nurses in ultrasound-guided techniques ensures higher proficiency and better outcomes, making it a vital skill in modern healthcare settings.
Improved Patient Comfort and Reduced Pain
Ultrasound-guided IV insertion significantly enhances patient comfort by minimizing pain and discomfort during the procedure. Real-time visualization allows nurses to avoid nerves and sensitive tissues, reducing the risk of accidental nerve injury. Patients with difficult venous access, such as those with fragile or deep veins, benefit from fewer insertion attempts, leading to less discomfort. The precision of ultrasound guidance also reduces the likelihood of multiple needle sticks, which are a common source of pain and anxiety. Additionally, the use of ultrasound can decrease the need for invasive procedures and complications, further improving the overall patient experience. This approach not only enhances patient satisfaction but also aligns with best practices in pain management and patient-centered care.
Longer Duration of IV Catheter Patency
Ultrasound-guided IV insertion is associated with a longer duration of catheter patency due to precise placement and reduced complications. The real-time visualization ensures proper positioning within the vein, minimizing the risk of catheter malposition or damage to surrounding tissues. This accuracy leads to fewer catheter-related complications, such as thrombosis or occlusion, which are common causes of premature catheter failure. Additionally, ultrasound guidance reduces the need for multiple insertion attempts, thereby decreasing venous trauma and inflammation. Properly placed catheters are less likely to become dislodged or infected, further extending their functional lifespan. As a result, patients benefit from fewer interruptions in treatment and improved overall care outcomes.
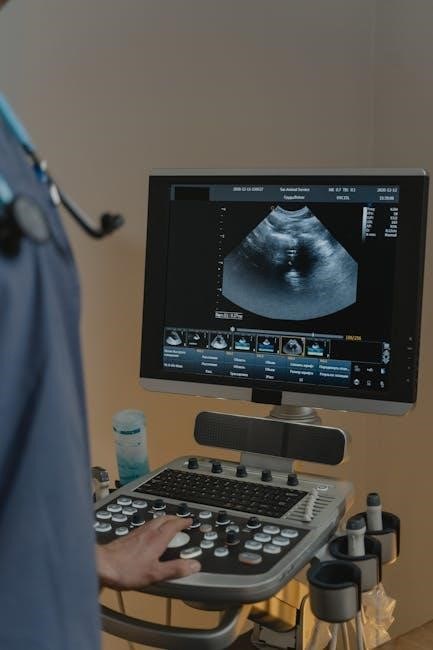
Definition and Overview of Ultrasound-Guided IV Insertion
Ultrasound-guided IV insertion, or USGPIV, uses real-time ultrasound imaging to enhance the accuracy of peripheral intravenous catheter placement, improving patient outcomes through minimally invasive techniques.
What is Ultrasound-Guided Peripheral Intravenous (USGPIV) Placement?
Ultrasound-Guided Peripheral Intravenous Placement (USGPIV) is a medical technique using real-time ultrasound imaging to guide the insertion of intravenous catheters into peripheral veins. This method enhances accuracy by providing direct visualization of veins, surrounding tissues, and the needle during insertion. USGPIV is particularly beneficial in patients with challenging venous access, such as those with obesity, dehydration, or peripheral vascular disease. By minimizing reliance on anatomical landmarks, it reduces complications like nerve or arterial punctures. The use of ultrasound ensures higher success rates, improved patient comfort, and longer catheter patency compared to traditional landmark-based methods. This approach is increasingly adopted in various healthcare settings, including emergency departments and intensive care units, to optimize vascular access outcomes. Nurses trained in USGPIV can perform the procedure systematically, ensuring safe and effective IV placement.
Basic Techniques for Sonographic Guidance
Basic techniques for sonographic guidance in IV insertion involve two primary approaches: the transverse and longitudinal methods. The transverse approach positions the ultrasound probe perpendicular to the vein, offering a clear cross-sectional view of the vein and surrounding structures. This method is beneficial for visualizing deeper or smaller veins. The longitudinal approach aligns the probe parallel to the vein, providing a detailed view of the needle trajectory. Both methods require precise probe positioning and needle alignment. Nurses are trained to adjust settings like depth and gain for optimal imaging. Proper technique ensures accurate needle placement, minimizing complications. These foundational skills are essential for effective ultrasound-guided IV insertion, particularly in challenging patient populations. Proficiency in these techniques enhances patient outcomes and clinical efficiency. Regular practice and feedback are crucial for mastery.

Key Skills and Training Requirements for Nurses
Nurses must master technical skills for operating ultrasound equipment and performing vascular assessments. Hands-on practice and feedback are essential for proficiency in ultrasound-guided IV insertion techniques.
Technical Skills for Operating Ultrasound Equipment
Mastering ultrasound equipment is vital for nurses. This includes understanding machine controls, optimizing image quality, and correctly using probes. Proper adjustment of depth, gain, and focus ensures clear vein visualization. Nurses must learn to differentiate between veins and arteries using Doppler and B-mode imaging. Proficiency in probe manipulation, such as transverse and longitudinal scanning, is essential for accurate vessel assessment. Training emphasizes identifying anatomical landmarks and navigating challenging patient anatomy. These technical skills are foundational for successfully guiding IV insertion, reducing complications, and improving patient outcomes. Regular practice and feedback refine these abilities, ensuring competence in ultrasound-guided procedures.
Clinical Skills for Vascular Assessment
Clinical skills for vascular assessment are critical in ultrasound-guided IV insertion. Nurses must evaluate patient anatomy, identify suitable veins, and assess venous depth and diameter. Proficiency in recognizing vein versus artery using Doppler imaging is essential. Nurses learn to adapt techniques for diverse patient populations, including those with challenging venous access. Understanding vein location, patency, and surrounding tissue is vital for successful cannulation. Training emphasizes patient-specific factors like obesity, dehydration, or edema that complicate vascular access. Clinicians are taught to optimize vein visibility through proper positioning and tourniquet use. These skills ensure accurate vessel selection, reducing insertion attempts and improving patient comfort. Effective vascular assessment is a cornerstone of ultrasound-guided IV placement, enhancing procedural success and minimizing complications;
Troubleshooting Common Challenges During USGPIV
During USGPIV, nurses may encounter challenges such as poor vein visualization, needle misplacement, or difficulty advancing the catheter. Adjusting ultrasound settings, using proper probe positioning, and optimizing patient anatomy can improve visualization. For patients with deep or small veins, a longer needle or different approach may be necessary. Complications like nerve or arterial puncture require immediate recognition and correction. Maintaining a steady hand and proper needle alignment is crucial. Troubleshooting also involves addressing patient-related factors, such as movement or anxiety, by ensuring comfort and clear communication. Regular practice and feedback help refine skills, reducing complications and improving outcomes. Effective troubleshooting ensures successful and safe USGPIV placement, enhancing patient care and procedural efficiency.

Step-by-Step Procedural Approach to USGPIV Placement
Prepare the ultrasound machine, position the patient, and select suitable veins. Use sonographic guidance to visualize the vein, insert the needle, and advance the catheter successfully.
Preparation and Positioning of the Ultrasound Machine
Begin by positioning the ultrasound machine directly in front of you for easy viewing without straining. Ensure the screen is at eye level and within reach. Power on the device and select the appropriate settings for vascular access. Use a high-frequency linear probe for clear imaging of superficial veins. Apply a small amount of gel to the probe to enhance image quality. Position the patient comfortably, with the arm extended and supported to facilitate vein visualization. Clean and prepare the skin with a chlorhexidine scrub to reduce infection risk. Have all necessary supplies, such as gloves, tourniquets, and catheters, readily available. Proper setup ensures efficiency and safety during the procedure.
Selection and Visualization of Suitable Veins
Begin by scanning the patient’s arm to identify suitable veins using the ultrasound machine. Look for veins that are appropriately sized and depth for catheter placement, typically between 0.3-1.5 cm deep. Use the ultrasound’s Doppler mode to confirm blood flow and distinguish veins from arteries. Adjust the machine’s depth and gain settings for optimal visualization. Scan from proximal to distal to identify the best insertion site. Use the transverse view to measure vein diameter and assess compressibility, ensuring the vein is not thrombosed or scarred. Switch to the longitudinal view to visualize the vein’s path and surrounding structures. Document the selected vein’s location and characteristics for future reference. Proper vein selection is critical for successful catheter placement and patient comfort.
Insertion Technique and Catheter Placement
Under real-time ultrasound guidance, insert the needle at a 20-30 degree angle, advancing it until the tip enters the vein. Use the ultrasound to confirm needle placement within the vein lumen. Once blood is aspirated, carefully thread the catheter over the needle, ensuring it is fully seated. Secure the catheter with sterile dressing and tape. Confirm catheter placement by flushing with saline and checking for easy flow. Proper technique minimizes complications and ensures patient safety. Always maintain sterility throughout the procedure to prevent infection. Adjust the catheter position if resistance is met, and consider using a different approach if difficulties arise. Successful placement is confirmed by ultrasound visualization and clinical assessment.

Common Complications and How to Avoid Them
Common complications include infiltration, nerve injury, and hematoma. Use real-time ultrasound guidance, ensure optimal needle angle, and assess patient anatomy to minimize risks and enhance safety.
Factors Complicating IV Insertion
Several factors complicate IV insertion, including obesity, dehydration, end-stage renal disease, peripheral vascular disease, diabetes, and intravenous drug use. These conditions often lead to difficult venous access due to reduced vein visibility or poor vascular integrity. Obesity can obscure veins, making landmarks and ultrasound visualization challenging. Dehydration causes veins to collapse, reducing accessibility. Patients with end-stage renal disease or peripheral vascular disease may have fragile or thrombosed veins, increasing the risk of complications. Diabetes can lead to peripheral neuropathy and altered tissue integrity, further complicating the procedure. Intravenous drug use often results in scarred or thrombosed veins, making successful IV placement more difficult. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing effective strategies to overcome them during ultrasound-guided IV insertion training.
Strategies to Minimize Risks and Complications
To minimize risks and complications in ultrasound-guided IV insertion, nurses should employ evidence-based strategies. Proper patient preparation, including hydration and positioning, improves vein accessibility. Using real-time ultrasound guidance enhances visualization, reducing the risk of accidental artery or nerve injury. Sterility should be maintained throughout the procedure to prevent infections. Selecting appropriate catheter sizes and avoiding over-the-needle catheters in fragile veins can reduce complications. Continuous monitoring during and after insertion helps identify and address issues promptly. Regular training and feedback improve technique and patient safety; Additionally, using chlorhexidine scrubbers to prepare the skin can enhance vein visibility, aiding successful insertion while minimizing risks.

Procedural Tips and Tricks for Successful USGPIV
Optimize ultrasound settings for vein visualization, ensure proper patient positioning, and maintain sterility throughout the procedure to enhance success rates and minimize complications during USGPIV insertion;
Optimizing Ultrasound Imaging for Vein Visualization
Adjusting the ultrasound machine’s gain and depth settings ensures optimal vein visualization. Proper probe positioning and technique, such as using a tourniquet, enhances image clarity. Maintaining appropriate pressure avoids vein compression. Skin preparation with chlorhexidine reduces artifacts, improving image quality. Positioning the machine for easy viewing streamlines the procedure; These strategies collectively enhance visualization and increase IV insertion success rates.
Best Practices for Maintaining Sterility and Patient Safety
Maintaining sterility and patient safety is paramount during ultrasound-guided IV insertion. Nurses should use sterile gloves, ensure the ultrasound probe is covered with a disposable sheath, and clean the skin with appropriate antiseptics. Proper hand hygiene before and after the procedure is essential. The insertion site must be kept sterile to prevent infection. Regularly disinfecting the ultrasound equipment and ensuring all materials are within their expiration dates further enhances safety. Adhering to these practices minimizes the risk of complications and ensures a safe, effective procedure for patients; Continuous training and adherence to clinical guidelines are critical for upholding these standards.

Simulation-Based Mastery Learning (SBML) in Training
Simulation-Based Mastery Learning (SBML) enhances nurses’ ultrasound-guided IV skills through realistic, repeatable practice. It allows for error-free learning in a controlled environment, improving patient safety and procedural confidence.
Role of Simulation in Improving USGIV Skills
Simulation-based training is a cornerstone in mastering ultrasound-guided IV insertion. By replicating real-world scenarios, it allows nurses to practice and refine their techniques without patient risk. Simulation environments provide hands-on experience with ultrasound equipment, enabling nurses to develop muscle memory and improve their ability to visualize veins and guide catheters accurately. Additionally, simulation models offer a controlled setting for addressing diverse patient scenarios, such as difficult venous access. This approach not only enhances procedural competence but also builds confidence and reduces anxiety, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and safer practices. Regular simulation training ensures that nurses stay proficient in USGIV techniques, adapting to new challenges and technologies in healthcare.
Curriculum Design for Effective Learning Outcomes
A well-structured curriculum is essential for ultrasound-guided IV insertion training. It should include foundational knowledge of ultrasound physics, vascular anatomy, and procedural steps. Hands-on simulation sessions allow nurses to practice vein visualization and catheter placement in a risk-free environment. Incorporating case-based learning and video demonstrations enhances understanding of diverse patient scenarios. Regular assessments and feedback ensure skill mastery. The curriculum should also emphasize patient safety, sterilization protocols, and troubleshooting common challenges. By integrating both theoretical and practical components, nurses gain confidence and competence in performing USGIV procedures effectively. Continuous feedback loops and competency-based progression ensure tailored learning experiences, ultimately improving patient care outcomes.
Continuing Education and Skill Sharpening for Nurses
Continuing education and skill sharpening are vital for nurses to stay updated on ultrasound-guided IV techniques, ensuring proficiency and incorporating feedback for enhanced patient care.
Resources and Recommendations for Further Learning
For nurses seeking to enhance their ultrasound-guided IV insertion skills, various resources are available. Academic journals like the Journal of Emergency Nursing and Critical Care Nursing offer evidence-based studies and practical insights. Simulation-based courses, such as those incorporating mastery learning, provide hands-on training. Practical guides and manuals, like those detailing systematic approaches, are invaluable. Online forums and communities dedicated to vascular access share tips and real-world experiences. Professional societies, such as the Association for Vascular Access, offer updated guidelines and training materials. Additionally, video tutorials and webinars on platforms like YouTube and medical education websites can supplement learning. These resources collectively support continuous improvement in ultrasound-guided IV insertion techniques.
Importance of Regular Practice and Feedback
Regular practice and feedback are essential for mastering ultrasound-guided IV insertion. Consistent practice enhances technical proficiency and clinical judgment, ensuring nurses can handle diverse patient anatomies and challenging cases. Feedback from experienced instructors helps refine techniques, improving accuracy and reducing complications. Simulation-based training allows nurses to practice in a risk-free environment, reinforcing skills and building confidence. Continuous feedback loops enable nurses to learn from mistakes, adapt to new scenarios, and improve patient outcomes. Regular practice also fosters muscle memory and efficiency, critical for timely and successful IV placements. By prioritizing practice and feedback, nurses can maintain high standards of care and stay proficient in this valuable skill;
USGPIV training revolutionizes nursing practice, enhancing patient care and IV success rates. Future advancements in technology and education will further refine skills, ensuring optimal outcomes and expanded accessibility.
Impact of USGPIV on Nursing Practice and Patient Care
Ultrasound-guided peripheral intravenous placement (USGPIV) has transformed nursing practice by significantly improving first-attempt success rates and reducing complications. Patients benefit from enhanced comfort, as the procedure often minimizes pain and anxiety associated with traditional methods. Nurses gain proficiency in handling difficult venous access cases, particularly in critically ill or pediatric patients. This technique fosters a patient-centered approach, aligning with modern nursing goals of precision and empathy. By integrating USGPIV into daily practice, nurses not only elevate their clinical skills but also contribute to better patient outcomes and satisfaction. The adoption of USGPIV underscores the importance of continuous learning and adaptation to advanced medical technologies in nursing care.
Emerging Trends and Innovations in Ultrasound-Guided IV Insertion
Recent advancements in ultrasound-guided IV insertion include the integration of artificial intelligence to enhance image clarity and automate vein detection. Portable, high-resolution ultrasound devices are becoming more accessible, enabling bedside procedures with greater precision. Simulation-based training platforms are increasingly adopted to refine nurses’ skills in real-time. Innovations in catheter design, such as echogenic materials, improve visibility under ultrasound, reducing placement errors. Additionally, AI-driven algorithms now predict vein depth and diameter, aiding in optimal needle placement. These trends not only streamline the process but also elevate patient safety and comfort, making ultrasound-guided IV insertion more efficient and reliable in diverse clinical settings. Such innovations underscore the evolving nature of this critical nursing skill.